Page Frame Allocation
物理内存分配器 Physical Memory Allocators
该部分的算法将在你需要时为你提供一个新的页面帧(Frame)。 此算法的客户端通常不在意具体返回的是哪个帧,尤其是,对多个帧的请求不需要返回连续帧 (除非你正在为DMA操作 ,例如网络数据包缓冲区,分配内存)。
以下文中N字母将代表以页面为单位的内存大小。
位图 Bitmap
使用N/8字节的大数组用作内存使用的位映射 (即,字节 #n 中的位 #i 定义了页 #n*8+i 的状态)。 设置给定页面的状态是快速的,时间复杂度为(O(1)),分配页面可能需要时间复杂度 (O(N))。
- uint32_t比较运算可以一次测试多达32位,从而加快分配速度
- 保留指向最后分配位的指针可能会提高下一次搜索的性能 (保留有关所有先前字节未成功搜索的事实的信息)
页面堆栈/列表
每个可用的物理帧的地址都存储在类似 栈 的动态结构中。 分配页面的速度很快,时间复杂度 (O(1)),也可以释放页面,但是检查页面的状态是不切实际的,除非存储了按物理地址排序的其他元数据。
大小部分方案 Sized Portion Scheme
你将每个区域 (例如16kb) 分成 (例如) 1 8kb和2 4kb的块。 然后你分发每一块。 通过这样做,你可以找到更接近精确尺寸的适合。 这意味着更少的浪费。 所以说你有32kb的面积
你甚至可以为每个部分提供1、2、甚至3或4 (或更多!) 类型的布局。 这样你就有更多的尺寸可供选择。
Buddy Allocation System 好友分配系统
这是linux内核的物理内存分配器。 请注意,linux有几个伙伴,具体取决于内存是否适合ISA DMA,还是来自 “高物理内存” 或只是 “正常”。 每个好友包含k个位图,每个位图指示可用的2 ^ i大小和2 ^ i对齐的自由页面块。 通常,linux使用从4k到512K块。
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
###.#....#........#...###...########.... real memory pattern
buddy[0]---> ###.#.xx.#xxxxxxxx#.xx###.xx########xxxx 5 free 4K , 5-byte bitmap
buddy[1]---> # # # . # . x x . # . # # . # # # # x x 5 free 8K , 20-bits map
buddy[2]---> # # # . # # # # # . 2 free 16K, 10-bits map
buddy[3]---> # # # # # 0 free 32K, 5-bits map
A buddy for N pages is about twice the size of a bitmap for the same area, but it allows a faster location of collections of pages. The figure above shows a 4-buddy with free pages/blocks denoted as . and used pages/blocks denoted as #. When a block contains at least one used sub-block, it is itself marked as used and sub-blocks that are part of a larger block are also marked as used (x in the figure). Say we want to allocate a 12-K region on this buddy, we'll look up the bitmap of free 16K blocks (which says we have one such starting at page #12 and another starting at page #36). buddy[2]->bit[4] is then set to 'used'. Now we only want 3 pages out of the 4 we got, so the remaining page is returned to the appropriated buddy bitmap (e.g. the single pages map). The resulting buddy is
0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
###.#....#..###...#...###...########.... real memory pattern
buddy[0]---> ###.#.xx.#xx###.xx#.xx###.xx########xxxx 6 free 4K , 5-byte bitmap
buddy[1]---> # # # . # . # # . # . # # . # # # # x x 5 free 8K , 20-bits map
buddy[2]---> # # # # # # # # # . 1 free 16K, 10-bits map
buddy[3]---> # # # # # 0 free 32K, 5-bits map
Note that initially, only the largest regions are available, so if buddy[0] is apparently empty, we need to check buddy[1], then buddy[2] etc. for a free block to be split.
混合方案
分配器可以被链接,以便 (例如) 栈 仅覆盖最后的操作,并且堆栈的 “底部” 被提交到位图 (用于紧凑存储)。 如果栈缺少页面,它可以扫描位图以找到一些 (可能在后台作业中)。
混合方案 #2
而不是只跟踪代表页的位,或者只跟踪 堆栈 上的页码,而是使用一个大的结构数组来表示内存。 在这些页面框架结构中,存储指向下一页的单个链接 (指针大小) 和指示其状态的8-16位信息块。 还包括虚拟页指针和页码所属的TCB。 保留指向每种类型页面的指针,指向列表的开始和结尾。 通过这种方式,你可以轻松地显示有关其内容的信息,每种类型的可用页数,混合类型,允许动态清理线程,相当容易地进行写复制,并保持页面的清晰简洁概述。 它也用作列出页面类型的反向页面映射表。
有关示例实现,请参见AtlantisOS 0.0.2或更高版本。
虚拟地址分配器
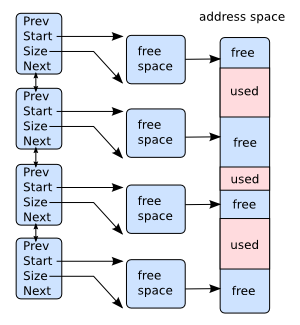
Flat List 平展列表
管理地址空间的大区域的一种直接方法是链表 (如下所示)。 每个 “自由” 区域都与给出其大小和基址的描述符相关联。 当需要分配某些空间时,使用 “第一拟合” 或 “最佳拟合” (或其他) 算法扫描列表以寻找足够大的区域。 这是例如ms-dos管理内存的方式。 分配内存时,适当的条目要么被删除 (整个区域被分配),要么被调整大小 (仅分配区域的一部分)。
请注意,对于平面链接列表,“是地址XXX的内存” 或 “在哪里可以得到一个大小为YYY的块” 问题可能需要对列表进行完整遍历才能得到答案。 如果虚拟内存变得支离破碎,列表变长,这可能会成为一个问题。 “地址XXX处的内存是免费的吗?” 主要用于在释放块时将两个空闲区域合并为一个新的 (更大的) 区域,并且如果列表由不断增长的地址保持顺序,则更容易处理。
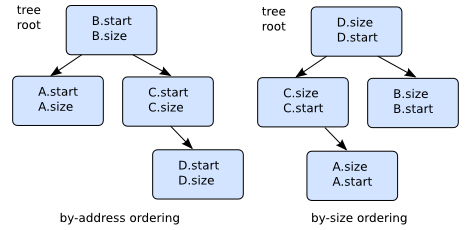
基于树的方法
由于经常在列表中搜索给定地址或给定大小,因此使用更有效的数据结构可能会很有趣。 其中一个仍然保持遍历整个列表的能力是AVL树。 AVL树中的每个 “节点” 将描述一个内存区域,并具有指向较低节点的子树和较高节点的子树的指针。
虽然在这样的平衡树中插入/删除需要比链表操作更复杂的操作,但通常使用O(log2(N)) 而不是O(N) 来搜索链表 -- 也就是说,如果你有1000个条目,则需要1000次迭代来扫描列表,以对照10次迭代来查找树中的给定间隔。
Linux使用AVL树进行虚拟地址管理已有相当一段时间了。 但是请注意,它将其用于区域 (例如在/proc/xxxx/maps中找到的内容),而不是用于类似malloc的接口。
另见
文章
- Memory Allocation
- Memory management
- Writing a memory manager - a tutorial
论坛主题
- Allocating memory for an allocator without an allocator
- A bitmap based allocation technique
- Ways to keep track of allocated RAM
- Questions about Memory Allocation
- Memory Management
- Memory Management to the X'th
- MM Questions
- (about)Tim Robinson Memory Management Tutorial #1
- Managing used/free pages
- Malloc, etc. (tute by curufir)
- Physical MM (by Freanan)
- Concepts and key points on alternative memory management schemes
外部链接
- mystran's Basic VMM for Dummies (cached)
- Page replacement algorithm on Wikipedia